Management and conservation of marine ecosystems
The teaching has two main axes: pollution and marine protection. The first part gives an overview of the pollution state in the North European waters (OSPAR areas) and their incidence on the marine fauna and human health, and it explains about the effects of manmade constructions on coastal communities. It also shows the actors of harmful plankton. The second part explains how to design marine protected areas in both temperate coastal areas, as also in vulnerable polar high seas areas. This teaching unit comes after the teaching about the structure and functioning of the marine coastal ecosystems in natural unpolluted conditions (or with very low pollution levels).
Course Contents
Two main objectives: learn how to evaluate the pollutions levels (1) and how to protect the costal ecosystems (2).
- Pollutions: Learning about the pollutions and man-made effects on marine coastal environments, and learn how to monitor the pollution level using various practical methods (AMBI, M-AMBI, IE2C, etc… Imposex levels and other DCE and DCSMM indices ).
- Pollutions types :
- Broad overview about the pollutions threatening the marine ecosystems
- Chemical pollutants: trace metals, radionucleids, Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAH), Organohalogens (PCBs), Dioxines & Furanes, Pesticides and other Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) such as TBT, plastic and litter…
- Biological pollutants: sewage and organic matter, eutrophication and harmful blooms
- Practical work on:
- Eutrophication and harmful phytoplancton species
- Persistent Organic Pollutants: Tributyltin (TBT) and Snail Imposex,
- AMBI, M-AMBI, IE2C calculations
- Large species surveys to analyze and to present.
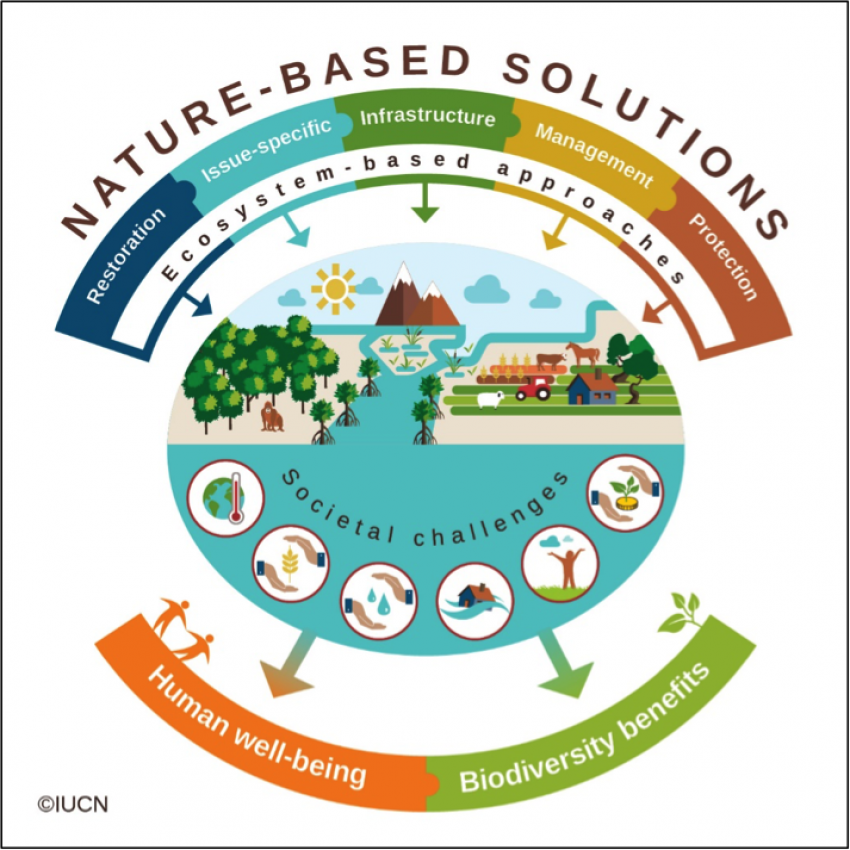
2. Marine conservation and protection: how to create effective marine protected areas (MPA).
- AMP at high Seas in the Antarctic areas : example of ROSS Sea
- Practical work in the classroom on dedicated articles
Final Competencies
1 To be able to assess the health quality of a marine ecosystem.
2 To know the prerequisites for creating an effective Marine Protected Area (MPA)
Additional information regarding teaching methods
- Lectures on dedicated topics (24hours)
- Seminars by skilled workers in environmental agencies, and from a natural marine park (6 hours).
- Practical works on indices from the sampling of the field to the work in the laboratory (identification of species, counting, dissections etc…) to the final calculation of the indices (36 hours).
Further course information can be found here: https://studiekiezer.ugent.be/studiefiche/en/C004309/2021